Welding specifications
Types of NDT (non destructive tests)
The NDT methods shall be carried out in accordance with the general principles given in EN 12062 and with the requirements of the standard particular to each method:
PT: penetrant testing according to EN 571-1;
MT: magnetic particle inspection according to EN 1290;
UT: ultrasonic testing according to EN 1714, EN 1713;
RT: radiographic testing according to EN 1435.
|
Table 1 - Abbreviation |
||||
|
The figure below shows the typical defects in welds.
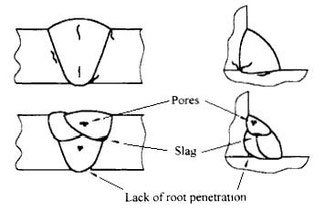
The NDT methods applied in testing of welded joints differ one from the other very much.
Visual inspection is the prior NDT method that should be done for the examination. The visual inspection provides basic information on the state of welded joints and the structure concerned.
Radiographic methods are most frequently used and permit a very reliable detection of three-dimensional discontinuities such as pores, non-metallic inclusions, incomplete penetration and undercuts at the inaccessible root side. The method seems to be less reliable in detecting planar, i.e. two-dimensional, defects such as cracks. The disadvantage of this method is the cost and that it requires particular skill for the realization.
The ultrasonic methods seem to be the most universally applicable. They may be applied to all types of defects but they are comparatively complicated and sensitive to various disturbances. They are less reliable, therefore, they are making themselves valued in welding very slowly.
Simple and reliable methods are available for detection of cracks reaching the surface. Magnetic methods are suitable for ferromagnetic materials, while penetrant methods are suitable for all metals.
The figure schematically shows the application of various NDT methods in testing butt and fillet welds.
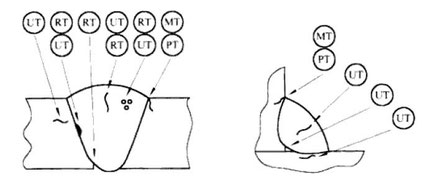
The Destructive and non-destructive controls shall be defined by the inspector and the Director of the work, taking into account these general rules
-
VT (visual inspection) on all the welds (100%)
-
PT (penetrant testing) or MT (magnetic particle inspection) applies to fillet welds and
partial welds
-
RT (radiographic testing) or UT (ultrasonic testing) applies to butt welds and
T-joints
RT generally is not suitable for fillet welds inspection.
The guidance in Annex C of EN 12062:1997 should be followed.
The generally accepted methods for examination of welds are given in table 2 for the surface imperfections and in table 3 for internal imperfections.
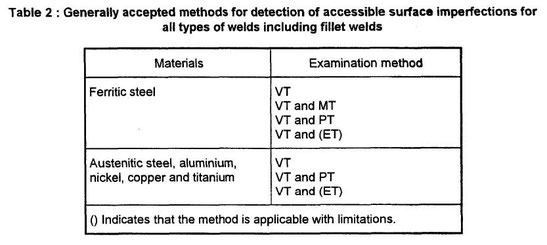
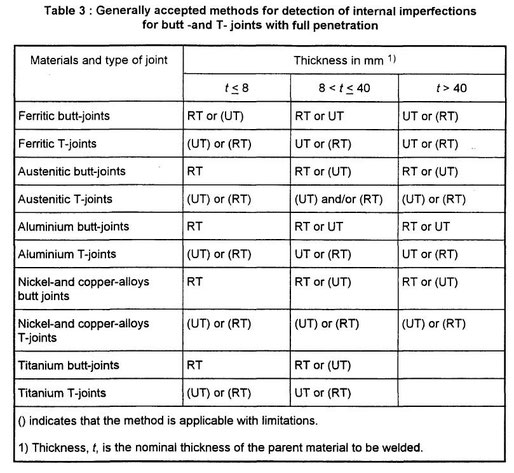
For partial penetration welds and fillet welds the unfused root can prevent satisfactory volumetric examination when using the methods given in table 3.
Techniques other than those given in tables 2 and 3 can be agreed for determining the actual degree of penetration and the dimensions of other imperfection types.
The following table reports a reference guide about the main NDT methods. The table is taken from the good article from NDTnet .
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Esko (Thursday, 15 August 2024 15:19)
Update old NDT/Inspection/Inspector standards